Arteries, Veins, and Capillaries
TW: brief mention of alcohol and drugs, mention of blood
Arteries, veins, and capillaries are all blood vessels. Blood vessels carry blood throughout the body and bleeding from different ones require different levels of care. Knowing about different types of blood vessels and how to respond to different types of bleeding as well as avoiding damaging major blood vessels can make self-harm safer.
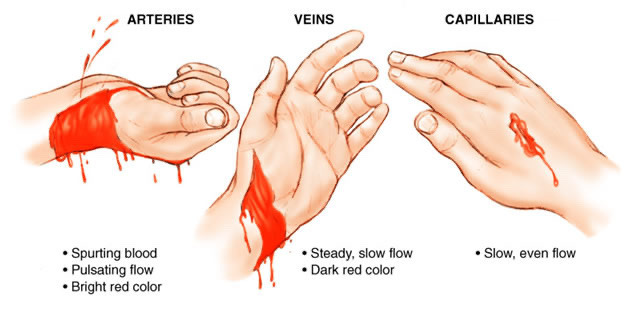
Telling the Difference
Capillaries
Capillaries are the smallest type of blood vessel and are also the least dangerous.
Capillary bleeding will...
- Bleed slowly and evenly
- Stop bleeding after 2-5 minutes of even pressure*
- Not typically life threatening*
Capillary bleeding will not...
- Spirt blood**
- Flow heavily*
*Unless you have a medical condition that affects bleeding (i.e. Haemophilia), have taken a blood thinning medication or drug, or been drinking alcohol.
**If a cut is spirting blood call an ambulance immediately and apply pressure, you may have hit an artery. This time of bleeding cannot be treated at home.
Veins
Veins carry blood back to your heart.
Venous bleeding will...
- Have dark red blood
- Have an even (not spurting) flow of blood
- Bleed more than capillaries
- Sometimes stops bleeding after 5-10 minutes of even pressure*
- Can be life threatening
*Unless you have a medical condition that affects bleeding (i.e. Haemophilia), have taken a blood thinning medication or drug, or been drinking alcohol.
Venous bleeding will not...
- Spirt blood**
- Be bright red
**If a cut is spirting blood call an ambulance immediately and apply pressure, you may have hit an artery. This type of bleeding cannot be treated at home.
Arteries
Arteries are the largest type of blood vessel; they carry oxygenated blood away from the heart. Arterioles are a type of artery; they bring oxygenated blood from larger arteries to capillaries. Cuts to arteries are always an emergency, if you (or someone else) are ever bleeding from an artery call for an ambulance immediately. Arterial bleeding can kill someone in minutes.
Arterial bleeding will...
- Spurt blood, like a fountain
- Have a pulsating flow in time with your heartbeat
- Bleed bright red blood
- Be deadly without immediate emergency medical attention (call an ambulance)
A cut to an artery cannot be treated at home and requires immediate emergency medical attention, call an ambulance. You can die from arterial bleeding in minutes.
First Aid
Call an ambulance if...
- The injury is spurting bright red blood; you have hit an artery
- You go into shock
- You lose sensation or movement in any area; this is a sign of nerve or tendon damage
- You have a medical condition that means you need immediate emergency medical attention for your injury
- You are unsure if you need immediate emergency medical attention
- If you do not think you can take care of your injuries alone and cannot get yourself to A&E
Go to A&E immediately if...
- The bleeding does not stop after 10 minutes of applying even pressure
- The injury is to a joint, palm, your face, or genitals
- The injury is internal
- You can see muscle or bone. Muscle looks like meat
- The tool you used to cut/scratch yourself was rusty
- You have a medical condition that means you need emergency medical attention for your injury
- You do not think you can take care of your injuries alone
Cuts that have are wide or gaping, are deeper than 0.5 inches/1.25 cm, or cuts where you can see fat (yellow lumps) or fascia (a thin white layer under the fat) should be stitched if possible. If you cannot get stitches use steri-strips, butterfly bandages, or zip-stitches to close the cut.
Even if you do not fit any of the above criteria you can still go to A&E for self-harm, thoughts of self-harm or suicide, or other mental health emergencies. Self-harm and thoughts of hurting yourself or others is always considered a medical emergency. If you are unsure how serious an injury is, call your local A&E's nurse line (if in the UK call 111 or use 111 online).
For capillary bleeding
Apply even pressure to the wound(s) with a clean cloth that will not get fluff in the wound (e.g. a bit of shirt) for ~5 minutes, or until bleeding stops. Tissue, toilet roll, or kitchen paper will get fluff in the wound and increase risk of infection. If you have been drinking or taken a drug/medication (such as alcohol) that can affect clotting apply pressure for 7-10 minutes.
If bleeding does not stop after 10 minutes of applying even pressure you need medical attention immediately, go to A&E. If you cannot get yourself to A&E safely, begin to have symptoms of shock, or think you might need immediate emergency medical care call for an ambulance.
Once bleeding has stopped, rinse the wound(s) with saline or warm water to remove any debris. Make sure your hands are clean. Dry the area well with a clean cloth that will not get fluff in the wound.
If a wound needs stitches (see above), seek immediate medical attention at A&E. If you cannot seek medical attention, use steri-strip, butterfly bandages, or zip-stitch to close the wound. These can also be used for more minor wounds where the edges of cut do not meet. Compound Benzoin Tincture can be used to help wound closures stick to the skin; apply a thin layer to the edges (not inside) of the cut and allow to dry before applying wound closure strips. Apply gauze or another wound covering on top of any steri-strips, butterfly bandages or zip stitches.
If the cut does not need stitches, use a plaster (band-aid), non-stick gauze, or other bandage to cover the wound.
More information on first aid and wound care for cuts here.
Losing blood can cause anaemia, as well as other health complications. An iron supplement can help prevent and treat anaemia. If you have symptoms of anaemia, think you have lost too much blood, or having other symptoms talk to your doctor.
For venous bleeding
Apply even pressure to the wound(s) with a clean cloth that will not get fluff in the wound (e.g. a bit of shirt) for ~7 minutes, or until bleeding stops. Tissue, toilet roll, or kitchen paper will get fluff in the wound and increase risk of infection. If you have been drinking or taken a drug/medication that can affect clotting.
If bleeding does not stop after 10 minutes of applying even pressure you need medical attention immediately, go to A&E. If you cannot get yourself to A&E safely, begin to have symptoms of shock, or think you might need immediate emergency medical care call for an ambulance.
Once bleeding has stopped, rinse the wound(s) with saline or warm water to remove any debris. Make sure your hands are clean. Dry the area well with a clean cloth that will not get fluff in the wound.
A cut to a vein needs stitches, seek immediate medical attention at A&E. If you cannot seek medical attention, use steri-strip, butterfly bandages, or zip-stitch to close the wound. Compound Benzoin Tincture can be used to help wound closures stick to the skin; apply a thin layer to the edges (not inside) of the cut and allow to dry before applying wound closure strips. Apply gauze or another wound covering on top of any steri-strips, butterfly bandages or zip stitches.
More information on first aid and wound care for cuts here.
Losing blood can cause anaemia, as well as other health complications. An iron supplement can help prevent and treat anaemia. If you have symptoms of anaemia, think you have lost too much blood, or having other symptoms talk to your doctor.
For arterial bleeding
Arterial bleeding CANNOT be treated at home and can kill you in minutes. Call for an ambulance immediately.
While you wait for the ambulance, apply pressure directly to the wound, (if possible) raise the wound above your heart, and follow the instructions of the emergency line operator.
Avoiding Major Blood Vessels
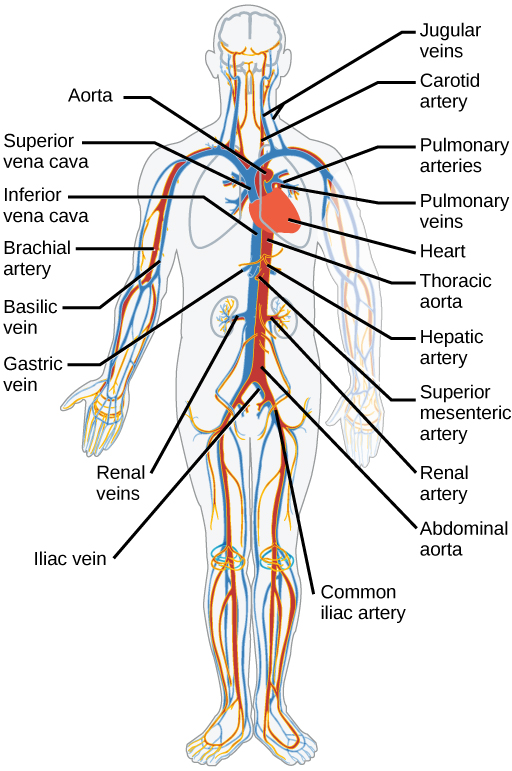
Some things can help you avoid hitting a major blood vessel...
- Knowing where veins and arteries are can help you avoid them. You can find diagrams for specific parts of the body online.
- Cutting in the same direction as veins and arteries makes you less likely to hit them.
- Avoid locations where arteries and veins are especially prominent, like on the wrists, groin, or neck.
- Avoid cutting deep. More major blood vessels are deeper in the skin.